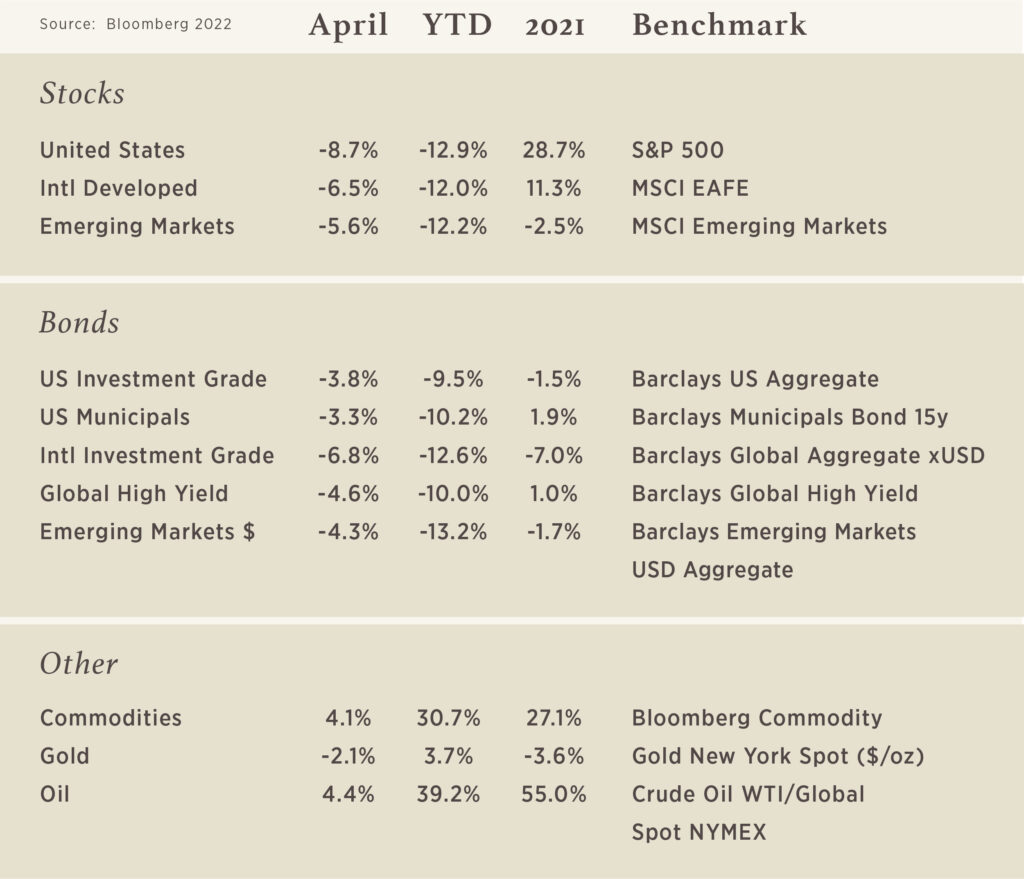
Chart of the Month
“Bonds are boring”. This is a quote from a client a few years ago and is a pretty good summary in most years. The start to 2022 is anything but boring in the bond market. Most investors recognize that a diversified portfolio should hold some bonds in their portfolios to provide protection at times of market stress. Wall Street likes to call this “risk-off”, meaning investors tend to exit equities for assets considered safer or less volatile when events rattle the markets.
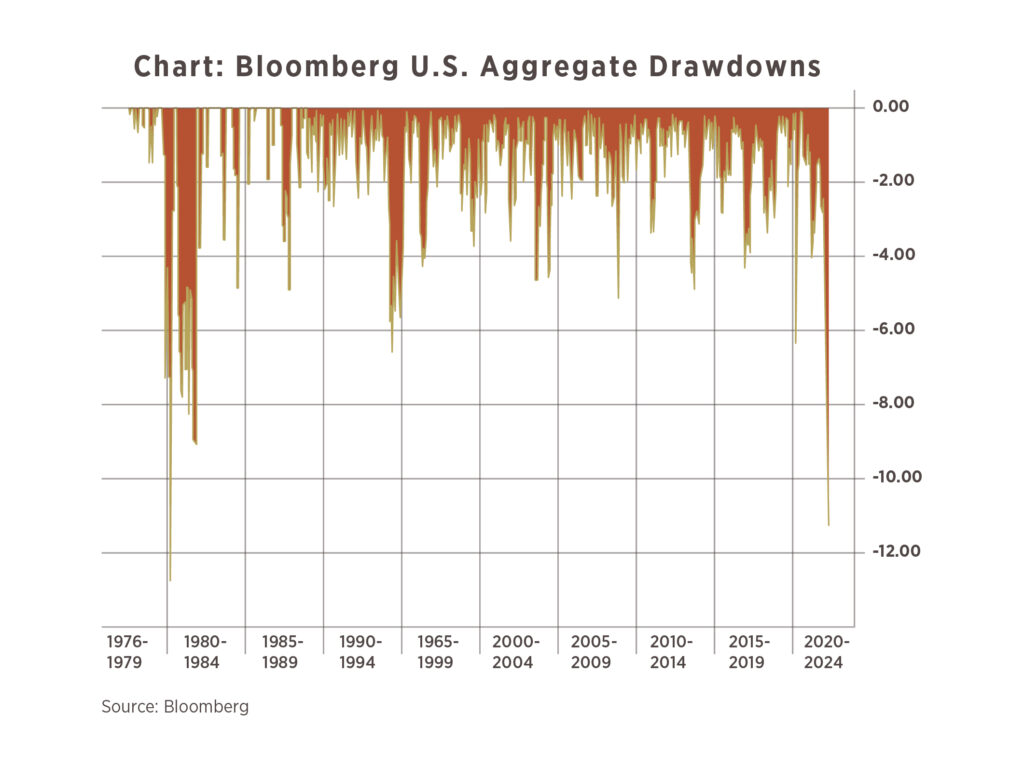
Given the declines in the stock market and the geopolitical tensions in Q1, it is reasonable to think that bonds should have provided some risk mitigation to portfolios, but in fact, bonds underperformed stocks in Q1. The US Fixed Income benchmark (U.S. Agg) is experiencing the second worst drawdown in its history, down 11.2% at its lowest point on 4/22/2022. So instead of being the ballast in a portfolio, it has been moving more in sync with equity markets during this year of volatility and exacerbating perceived losses.
Why has this happened? The bond market quickly priced in a significant increase in interest rates – which in turn led to lower fixed income prices. We believe this move down in bond prices is due to higher rates and not due to declining credit quality or higher default risk.
What can you expect moving forward? We believe that most of the increase in long-term rates is likely behind us. As a result, bond prices should be more stable and investors should benefit from higher rates and income going forward.


Understanding Extended Care
The important question: are you prepared?
Addressing the potential threat of extended care expenses may be one of the biggest financial challenges for individuals who are developing a retirement strategy.
The Administration for Community Living estimates that by 2060, 94.7 million Americans will be aged 65 and older. Of those, it’s estimated that someone who just turned 65 has an almost 70% chance of needing some type of extended care.1,2
What Is Extended Care? Extended care is not a single activity. It refers to a variety of medical and non-medical services needed by those who have a chronic illness or disability that is most commonly associated with aging.
Extended care can include everything from assistance with activities of daily living, like providing help with dressing, bathing, using the bathroom, or even driving to the store. Extended care may also include more intensive therapeutic and medical care requiring the services of skilled medical personnel.
Extended care may be provided at home, at a community center, in an assisted living facility, or in a skilled nursing home. It’s also important to recognize that extended care is not exclusively for the elderly; it is possible to need extended care at any age.
How Much Does Extended Care Cost? Extended care costs vary state by state and region by region. The national average for extended care can cost anywhere from $50,000 to $100,000 or more a year. The cost for a home health aide starts at an average of $20 per hour, but can be expected to increase if skilled nursing is involved.3
Individuals who would rather not burden their family and friends have two main choices for covering the cost of extended care: they can choose to self-insure or they can purchase extended-care insurance.
Many self-insure by default, simply because they haven’t made other arrangements. Those who self-insure may depend on personal savings and investments to fund any extended care needs. The other approach is to consider purchasing extended care insurance, which can cover all levels of care, from skilled care to custodial care to in-home assistance.
Several factors will affect the cost and availability of extended-care insurance, including age, health, and the type and amount of insurance purchased. You should consider determining whether you are insurable before implementing a strategy involving extended-care insurance. Any guarantees associated with a policy are dependent on the ability of the issuing company to continue making claim payments.
When it comes to addressing your extended care needs, many look to select a strategy that may help them protect assets, preserve dignity, and maintain independence. If those concepts are important to you, consider your financial approach to extended care.
This material was prepared by MarketingPro, Inc., and does not necessarily represent the views of the presenting party, nor their affiliates. This information has been derived from sources believed to be accurate. Please note – investing involves risk, and past performance is no guarantee of future results. The publisher is not engaged in rendering legal, accounting or other professional services. If assistance is needed, the reader is advised to engage the services of a competent professional. This information should not be construed as investment, tax or legal advice and may not be relied on for the purpose of avoiding any Federal tax penalty. This is neither a solicitation nor recommendation to purchase or sell any investment or insurance product or service, and should not be relied upon as such. All indices are unmanaged and are not illustrative of any particular investment.
Citations
1. ACL.gov, July 28, 2020
2. ACL.gov, February 18, 2020
3. AARP.org, November 20, 2020