LEVEL ONE
Must Haves
Goal: Plan for and document the transfer of assets with minimized tax and transfer cost.
A Will
A will appoints guardians for your children and spells out specifically how you want your property split.
A Living Trust
A living trust avoids probate, allows for privacy, and designates how assets are to be divided upon your death.
A Healthcare Power of Attorney
Designate a healthcare agent to make decisions in the event you are unable to make them for yourself.
A Financial/Property Power of Attorney
Designate an agent to make financial decisions in the event you are unable to.
Review co-ownership provisions & account titling
It is important to review joint accounts that transfer to a designated person upon death.
Periodically review beneficiary designations
This is important as some assets (such as IRAs, Life Insurance, and Annuities) pass to your designated beneficiaries.


LEVEL TWO
Considerations
Goal: Further enhance the direction of assets, minimize estate taxes or increase asset protection
Grantor Retained Annuity Trusts
Grantor Retained Annuity Trusts (GRAT) seek to pass assets to beneficiaries free of estate and gift tax that have appreciated over the IRS Section 7520 interest rate.
Explore Charitable Options
Explore Charitable Trust, Donor-Advised Fund and Foundation Options.
Irrevocable Life Insurance Trust
Because life insurance is not necessarily estate tax free, consider establishing an Irrevocable Life Insurance Trust.
Qualified Personal Residence Trust
A Qualified Personal Residence Trust (QPRT) is a type of trust that allows its creator to remove a personal home from his or her estate.
Spousal Lifetime Access Trusts
Spousal Lifetime Access Trusts (SLATs) seek to allow spouses to pass assets to each other and other loved ones free of estate and gift tax while maintaining limited, indirect access to the assets.
Intra-Family Loans
Intra-Family Loans can provide family members lower borrowing rates than traditional financing options.
Special Needs Trusts
Ensure the proper passing of assets to ensure beneficiaries with special needs are not disqualified from entitled benefits.
LEVEL THREE
Advanced
Goal: Options for Complex Estate Tax Issues or Liability Concerns
Self-Cancelling Notes
Self-Cancelling Notes allow the exchange of property for periodic payments based upon mortality.
Trust-Friendly Jurisdictions
Certain states, including Delaware, have favorable trust statutes, offering the potential to pass assets across generations without incurring transfer taxes (Dynasty Trusts), delegate responsibilities to non-trustees (Directed Trusts), protect assets and more.
Family LLPs & LLCs
Family Limited Liability Partnerships and LLCs provide legal, financial, and tax structure to family businesses.

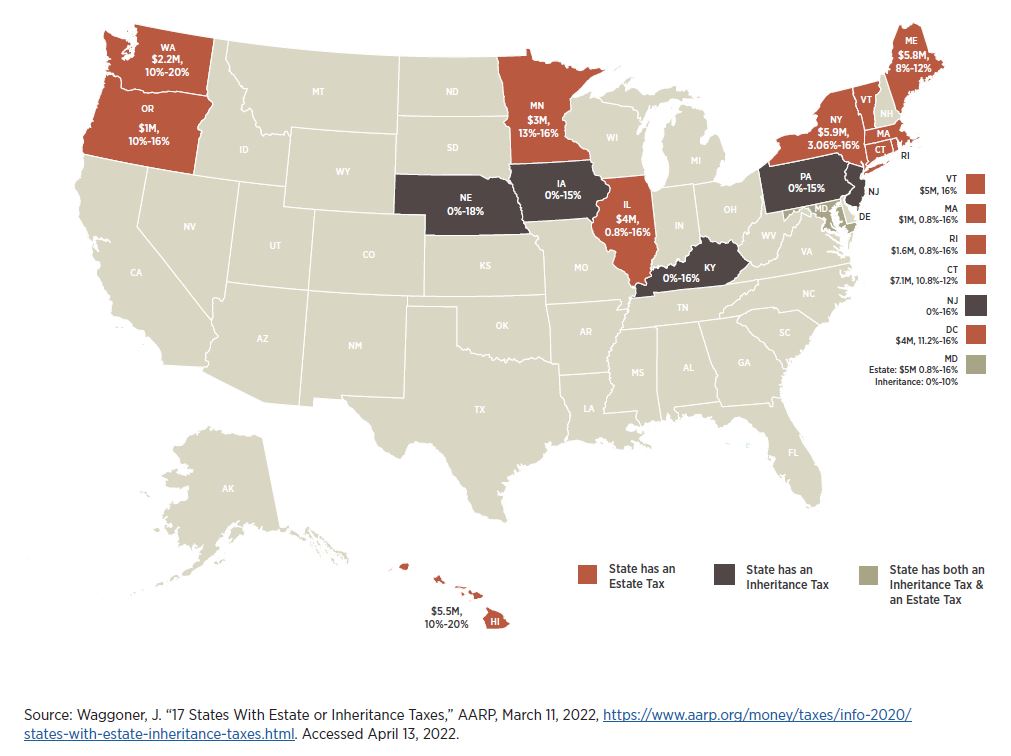
How Assets Pass Upon Death
Probate vs Non-Probate Assets
Probate is a public-court process that helps settle legal and financial matters upon death according to a will, if written.
Court costs, length of time, the lack of privacy and family disagreements are all potential issues that may arise within the probate process. With proper estate planning, you can limit the amount of assets that pass through probate.
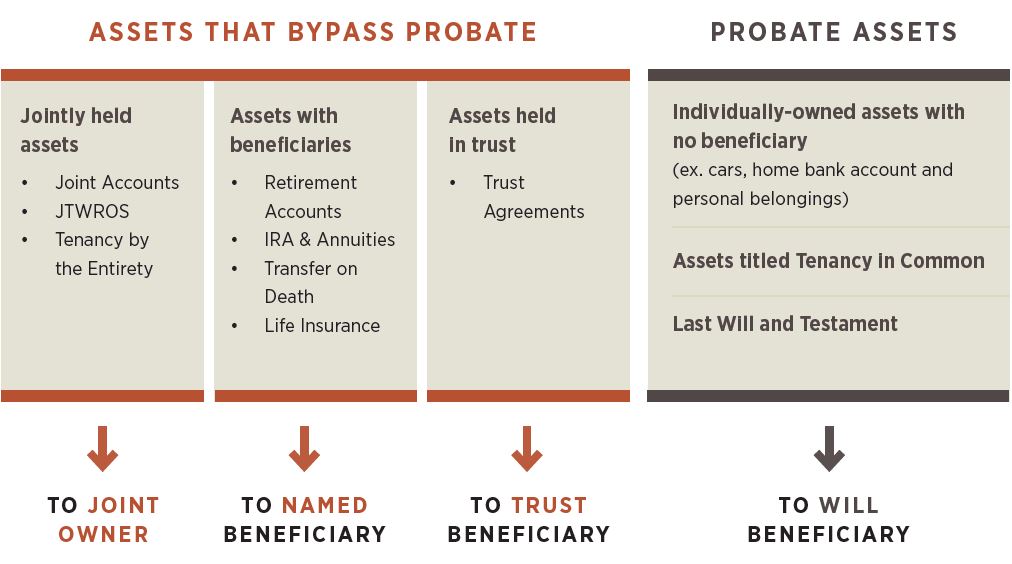

How Assets Pass Upon Divorce
Marital vs Non-Marital Assets
Estate planning is not divorce planning. Without a pre- or post-nuptial agreement, marital assets are subject to equitable division in a divorce proceeding.
Effective for divorces finalized after January 1, 2019, alimony payments will no longer be tax-deductible by the paying spouse and will not be added to the taxable income of the receiving spouse.
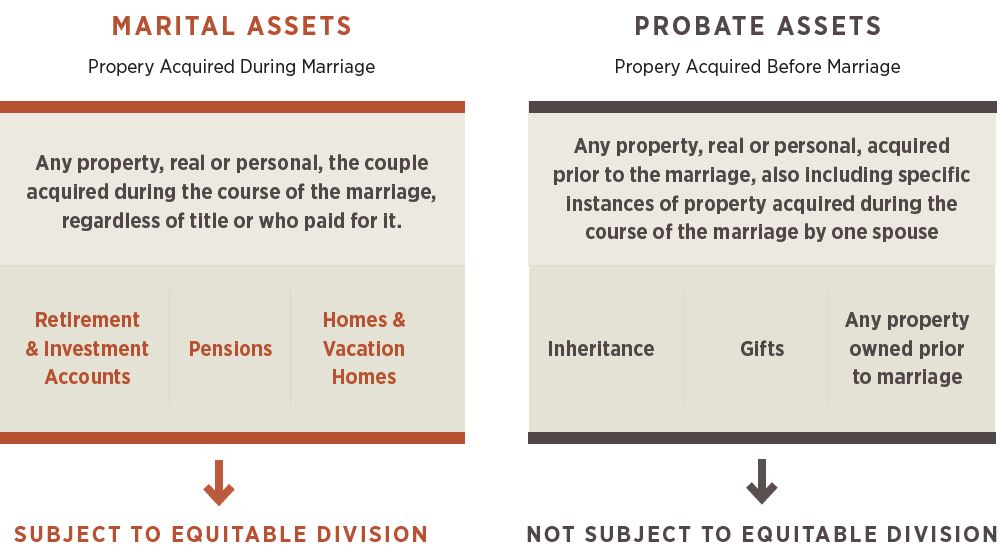

Estate Planning Updates
A Window of Opportunity
- The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) of 2017 significantly increased the estate exclusion amount (presently $12.06 million for 2022), though there had been concern that individuals taking advantage of the higher exclusion amount might one day owe additional tax for prior gifts, should the estate exclusion decrease after 2025.
- The Treasury Department and IRS later issued final regulations that individuals utilizing the increased gift and estate tax exclusion amounts from 2018 to 2025 would not be adversely impacted after 2025, should the exclusion revert to pre-2018 levels.
- Key Takeaway: Individuals who have, or are likely to have, a taxable estate and who have sufficient assets to fund expenses during their lifetime may want to consider gifting additional assets to loves ones while the increased exclusion amount still stands.
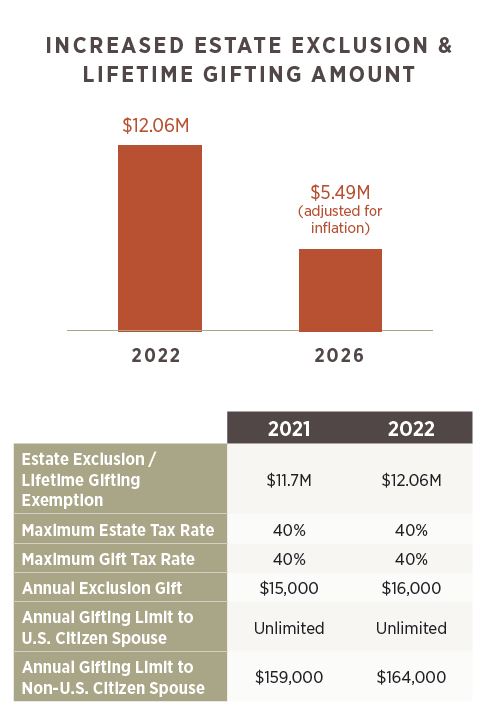
Don’t Forget Estate Tax at the State Level!
Many states have estate exclusions far below the federal level which may result in state estate taxes. Older estate plans should be reviewed to ensure trust provisions incorporate current federal and state estate tax limits.